
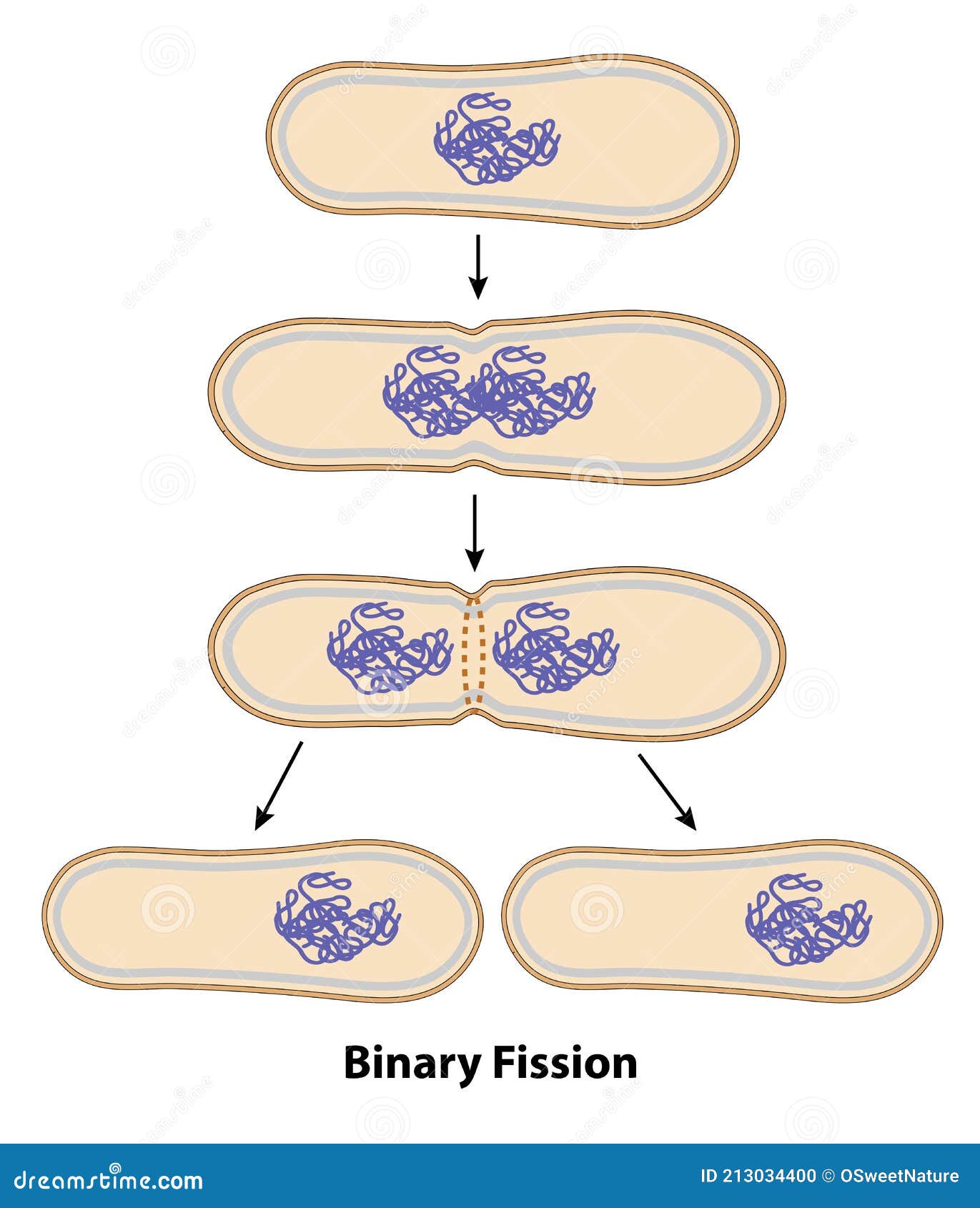
Oblique: It occurs in dinoflagellates like Ceratium.Here, the cell division occurs at a horizontal axis. Transverse: It commonly occurs in ciliates like Paramecium.Here, the cell division occurs along a vertical axis that divides a cell’s nucleus and cytoplasm longitudinally. Longitudinal: It occurs in flagellates (like Euglena) and ciliates (like Vorticella).But, it always happens at right angles to the expanding nucleus. The plane of cell division is variable, or it occurs along any axis. Irregular: It occurs in amoebae having irregular symmetry.Using binary fission, the cell can divide irregularly, transversely, longitudinally and obliquely.It does not give any genetic variability to offspring, as they are identical.Binary fission occurs to increase the population of organisms.Besides prokaryotes, some simple eukaryotes and eukaryotic cell organelles may also undergo binary fission.Offspring produced by binary fission are genetic clones of their parents.Once a septum forms completely, the cell splits into two identical daughter cells.Later, the exchange of cytoplasmic material occurs between the separating cells. A septum begins to form between the cell, which constricts the cell into two.Then, the cell elongates, and the DNA is copied.First, the parent cell duplicates its DNA from the origin of replication.In contrast, DNA replication in mitosis occurs during the S-phase, long before its separation in the M-phase.īinary fission is common in prokaryotes like bacteria, archaea and eubacteria etc. Then, the DNA separation co-occurs with DNA replication during binary fission in prokaryotes.But, the cells undergoing mitosis form mitotic spindles, which orchestrate the DNA movement. First thing, prokaryotes do not undergo karyokinesis, which means they cannot form a mitotic spindle.The cell divides its cytoplasm to form two new cells.īut, the mechanism of the two processes is relatively different.In both cases, chromosomes are copied and separated.It shares some common features with the mitosis (an asexual method that occurs in eukaryotes) like: Binary fission is one of the asexual reproduction methods. It is a cell-reproduction method that duplicates the parent cell into two identical offspring or daughter cells.
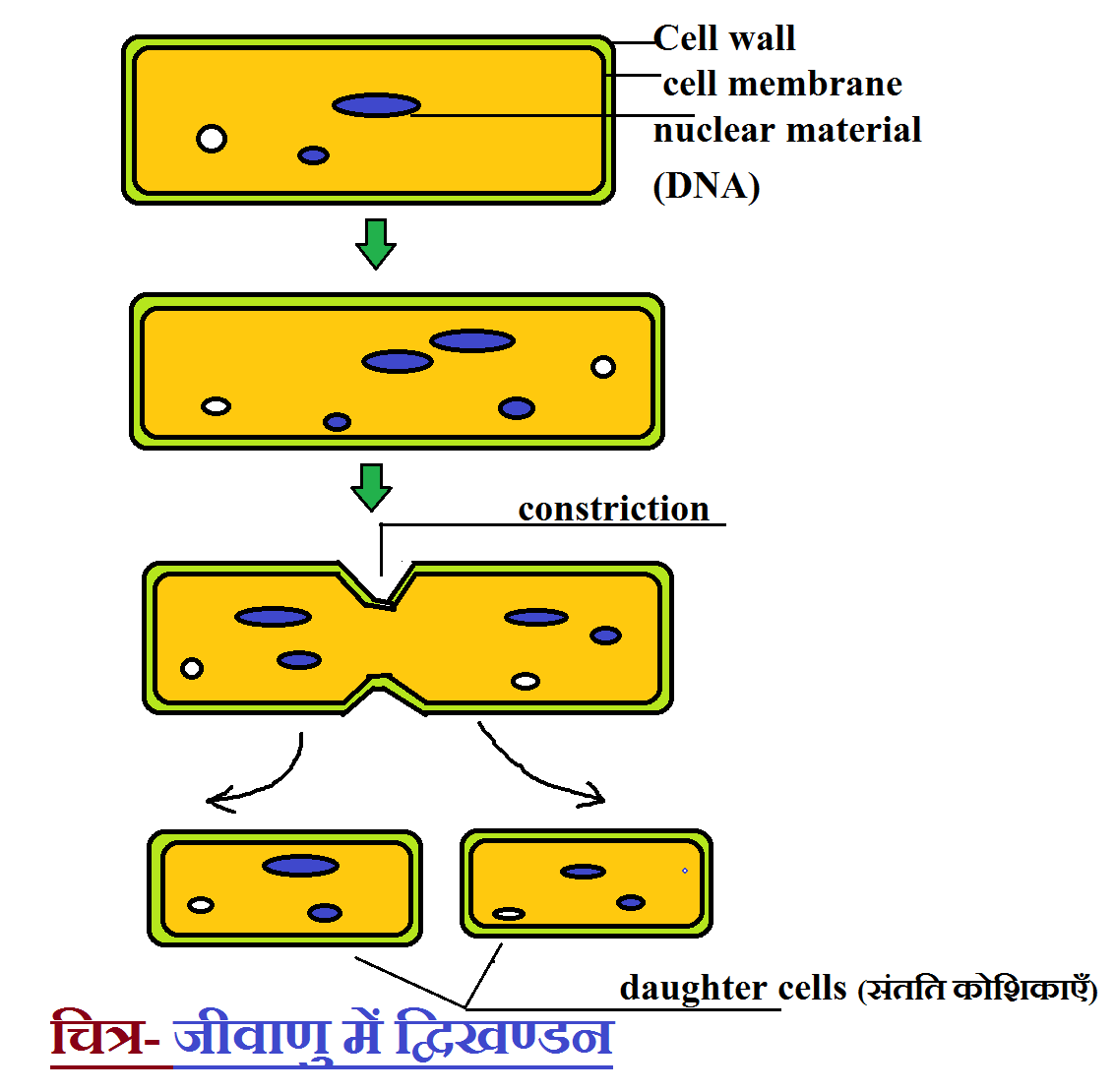
Also, you will get to know the process of binary fission in different organisms. This post describes the meaning, steps and types of binary fission. The process of binary fission prevalently occurs in prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), single-celled eukaryotes (protozoans) and some eukaryotic cell organelles (mitochondria). Here, an important thing to note is that these daughter cells are genetic clones of a parent cell. So, we can say that binary fission is the process of cell splitting into two daughter cells. The term binary is marked by a number two, and fission is the splitting or breaking up of something into parts. By breaking the term binary fission, we can define the term easily. Also, the new individuals have the potential to grow up to the size of a parent cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
